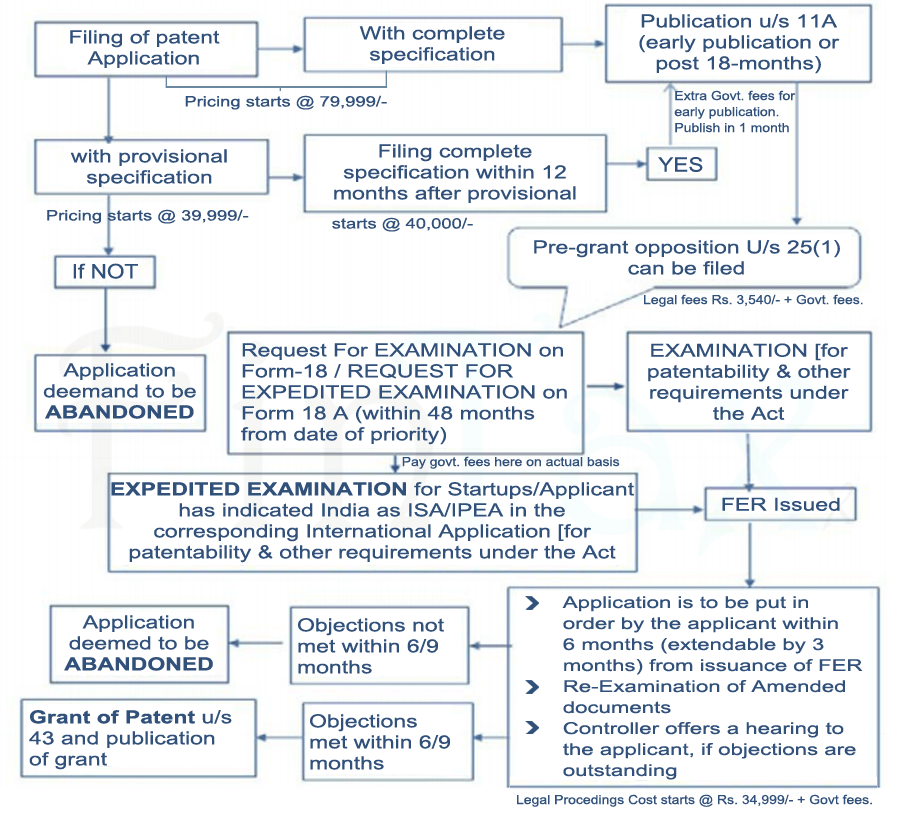
-
Why do you need FinTax Corporate Professional's service ?
- Drafting a patent application is a specialised job and requires both technical (field of invention) and legal (Indian patent act) understanding.
As you know, patent is a techno-legal document. Many inventors trying to write patent application on their own writes it from completely technical perspective. Writing patent application as a technical document without considering legal aspect may be a mistake which can make your application not worth a lot. And all the efforts you took for research and development can go waste.
Hence, right patent professional (or patent agent) with appropriate experience can remarkably add value to patent application.
FinTax Patent Professional is the right choice to get your Patent registration success.
-
Is FinTax Patent Professional works in all State for Patent Registration?
- Yes. We do serve our clients PAN India from our Branch Offices and Associate Patent Professionals in Major Cities.
-
How much time taken to get the Patent Application filed?
- Provisional Patent Application filing takes 7-10 days
Complete Patent Application Filing Takes 12-15 days
-
Does Indian Patent give protection worldwide?
- No. Patent protection is a territorial right and therefore it is effective only within the territory of India. There is no concept of global patent.
However, filing an application in India enables the applicant to file a corresponding application for same invention in convention countries or under PCT, within or before expiry of twelve months from the filing date in India. Patents should be obtained in each
country where the applicant requires protection of his invention.
-
What can be patented?
- An invention relating either to a product or process that is new, involving inventive step and capable of industrial application can be patented. However, it must not fall into the categories of inventions that are non- patentable under sections 3 and 4 of the Act.
-
What is the criteria of patentability?
- An invention is patentable subject matter if it meets the following criteria -
i) It should be novel.
ii) It should have inventive step or it must be non-obvious
iii) It should be capable of Industrial application.
iv) It should not attract the provisions of section 3 and 4 of the Patents Act 1970.
-
When should an application for a patent be filed?
- An application for a patent can be filed at the earliest possible date and should not be delayed. An application filed with provisional specification, disclosing the essence of the nature of the invention helps to register the priority of the invention. Delay in filing an application may entail some risks such as:
(i) some other inventor might file a patent application on the said invention and
(ii) there may be either an inadvertent publication of the invention by the inventor himself/herself or by others independently of him/her.
-
Can any invention be patented after publication or display in the public exhibition?
- Generally, an invention which has been either published or publicly displayed cannot be patented as such publication or public display leads to lack of novelty. However, under certain circumstances, the Patents Act provides a grace period of 12 months for filing of
patent application from the date of its publication in a journal or its public display in an exhibition organised by the Government or disclosure before any learned society or published by applicant. The detailed conditions are provided under Chapter VI of the Act
(Section 29-34).
-
Does the Patent Office keep information of the invention secret?
- Yes. All the patent applications are kept secret upto 18 months from the date of filing or priority date whichever is earlier and thereafter they are published in the Official Journal of the Patent Office which is published every week and also available on the IPO
website. After its publication, public can inspect the documents and also may take the photocopy thereof on payment of the fee as prescribed.
-
Is it necessary to visit the Indian Patent Office to transact any business relating to patent application?
- It is not necessary to visit the patent office to file the application as online filing facility is provided. Only in case the application is required to be filed offline, the same can be filed physically at the counter of the Office. Moreover, all the communications with the office are made through emails. However, hearing proceedings relating to patent application can be attended with prior appointment on any working day during prosecution stage.
-
Where can one find the information relating to published/ granted patent
application?
- The information relating to the patent application is published in the Patent office Journal issued on every Friday. This is also available in electronic form on the website of the Patent Office, www.ipindia.nic.in.
-
Who can apply for a patent?
- A patent application can be filed either by true and first inventor or his assignee, either alone or jointly with any other person. However, legal representative of any deceased person can also make an application for patent.
-
How can I apply for a patent?
- A patent application can be filed with Indian Patent Office either with provisional specification or with complete specification along with prescribed Govt fee.
In case the application is filed with provisional specification, then one has to file complete specification within 12 months from the date of filing of the provisional application. There is no further extension of time to file complete specification after expiry of said period.
-
How can one register for online filing of patent application?
- To register for filing of patent application, the user is required to obtain the Class III digital signature. After obtaining the digital signature, the user can register himself on the CGPDTM website by creating his user ID and password.
-
Is there any jurisdiction for filing patent application in India?
- Yes, India has four patent offices located at Kolkata, New Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai. Each office has a separate territorial jurisdiction. The appropriate office for all proceedings including filing of the application depends normally where the applicant/first mentioned applicant resides/has domicile/has place of business/has origin of invention. In case of foreign applicants, it depends on the address for service in India given by such applicant.
-
When can an applicant withdraw patent application in India?
- In India, a patent application can be withdrawn in the following ways:
1) A request for the withdrawal of the application can be filed within 15 months of the date of filing or date of priority, whichever is earlier and accordingly the application
will not be published and be treated as ―withdrawn‖.
2) An applicant can withdraw the application before the issuance of the First Examination Report. However, on withdrawal of the application, applicant can
claim a refund of up to 90% of examination fees.
3) An applicant can withdraw the application any time after its filing but before the grant of patent by making a request. There is no fee for withdrawing the application. And also there is no refund of examination fee.
CONTACT FinTax PATENT PROFESSIONAL FOR THIS.
-
Is it necessary to file a provisional application?
- Generally, when an invention is not complete an application can be filed with provisional.
Specification which is known as provisional application. This is useful in establishing a priority date for your invention. Moreover, it also gives sufficient time to the applicant to assess and evaluate the market potential of his invention before filing complete
specification. However, it is not necessary to file an application with provisional specification and one can file application directly with complete specification.
-
When is an application for patent published?
- Every application for patent is published after expiry of 18 months from the date of its filing or priority date whichever is earlier. However, following applications are not published.
A) Application in which secrecy direction is imposed,
B) Application which has been abandoned u/s 9(1) and i.e when a provisional, application has been filed and the complete application has not been filed with 12 months from the filing of the provisional application,
C) Application which has been withdrawn 3 months prior to 18 months
-
Is there any provision in the Patents Act for early publication?
- Yes, the applicant can make a request for early publication in Form 9 along with the prescribed fee. After receiving such request the Patent Office publishes such application within a period of one month provided the invention contained thereon does not relate to
Atomic energy or Defence purpose.
CONTACT FinTax PATENT PROFESSIONAL FOR THIS.
-
Is patent application once filed examined automatically?
- A patent application is not examined automatically after its filing. The examination is done only after receipt of the request of examination in Form 18 either from the applicant or from third party or Form 18A for expedited examination (under conditions as prescribed in the Rules).
-
When can the request for examination be filed?
- The request for examination can be filed within a period of 48 months from the date of priority or date of filing of the application whichever is earlier. For more details kindly refer to rule 24B of the Patents Rules 2003 as amended.
-
What happens to a patent application once it is examined?
- After examination, the Patent office issues an examination report to the applicant which is generally known as First Examination Report (FER). Thereafter the applicant is required to comply with the requirements within a period of 6 months from the date of FER which can be extended by 3 months (There is no provision for extension of time beyond the said period and the application is deemed to have been abandoned).In case, the application is found to be in order for grant, the patent is granted, provided there no pre-grant opposition is filed or pending. A letter patent is issued to the applicant. However, in case a pre-grant opposition is pending, the further action is taken after disposition of the pre-grant opposition.
-
Does an applicant get an opportunity of being heard before his application is refused?
- If the applicant does not file a reply within 6 months or does not take an extension of 3 months, the application is deemed to have been abandoned.
-
Is there provision for extension beyond time limit of 9 months?
- If applicant has not complied with the requirements within the prescribed time, the Controller shall provide an opportunity of being heard to the applicant before refusing his application if a request for such hearing has been made by the applicant at least 10 days in advance before expiry of the statutory period.
-
What is time limit for filing the representation for pre-grant opposition?
- A representation for pre-grant opposition under section 25(1) of Patents Act, 1970 can be filed, on Form 7A within six months from the date of publication of the application u/s 11A or before the grant of patent.
-
Is it possible to file pre-grant opposition even though there is no request for examination filed?
- Yes, it is possible to file representation for pre-grant opposition even though there is no request for examination has been filed. However, the representation will be considered only when a request for examination is received within the prescribed period.
-
Is there any fee for filing such representation for pre-grant opposition?
- No, there is no fee for filing representation for pre-grant opposition. This can be filed by any person.
-
What is the time limit for filing post-grant opposition in the patent office?
- The time for filing post-grant opposition is 12 months from the date of publication of the grant of patent in the official journal of the patent office.
-
Is there any fee for filing post-grant opposition?
- Yes, the post grant opposition has to be filed in the prescribed Form 7 along with prescribed fees as mentioned in First Schedule in Patents Rules 2003.. The post grant opposition has to be filed by the person interested and not by any other person
-
What are the e-filing facilities available for Patent on Website of IP India (www.ipindia.nic.in)?
- The following are the e-filing facilities available for an applicant:
• Comprehensive e-filing facility for Patents and Designs,
• Comprehensive payment gate way including net banking, payment by Debit/Credit card
• Web based Simple Registration process and filing procedure
• Real time Validations with IPO Patent database
• Manage User Profile and Folders
• 10% fee reduction on online filing compared to offline filing to promote online filing.
• Request for expedited examination- only through e-filing
-
Does patent office help in finding users for patent?
- The Patent Office has no role beyond grant of patent. Since patents are private rights the patent owner is responsible for commercialising the patent either himself or through licensee. However, the information relating to grant of patent is published in the Patent Office journal and also published on the Patent Office website which is accessible to the public worldwide. This certainly may help the applicant to attract potential user or licensee. The patent office also compiles and updates a list of patents which are lapsed/ceased in India.
-
Is Indian patent database searchable? How can one find out whether an invention is already patented?
- The person concerned can perform a search free of cost on Indian Patent database consisting of published patent applications and granted patents. The said database is available on Patent Office website http://ipindiaservices.gov.in/publicsearch. Further, the website (www.ipindia.nic.in) contains innovative tools under DYNAMIC UTILITIES which gives information about the patent applications at various stages of processing.
-
Is there any difference in the amount of fees to be paid by an individual or a legal entity for filing a patent application?
- Yes, the Patent Rules provides for different fee for individuals/Startups, SME‘s and legal entity. Details can be seen in the First Schedule of the Patents Rules, 2003 as amended from time to time.
-
What are obligations of the patentee after the grant of patent?
- After the grant of patent, every patentee has to maintain the patent by paying renewal fee every year as prescribed in the schedule I. For first two years, there is no renewal fee. The renewal fee is payable from 3rd year onwards. In case the renewal fee is not paid the patent will be ceased.
-
Can the patentee pay renewal fee at a time or has to pay every year?
- The patentee has choice to pay the renewal fees every year or he can pay in lump sum as well.
-
When can a patent be restored after its cessation?
- A request for restoration of patent can be filed within 18 months from the date of cessation of patent along with the prescribed fee. After receipt of the request the matter is notified in the official journal for further processing of the request.
-
Is it necessary to engage a registered patent agent for filing an application for patent?
- It is not necessary under the patent law to engage a registered patent agent for filing an application for patent. The applicant is free to file an application by himself or through the patent agent. However, an applicant who is not a resident of India is required to file either through the registered patent agent or must give an address for service in India
-
Is it mandatory to obtain prior permission from the Patent Office to file application for patent outside India or abroad?
- Ordinarily, under the following circumstances, it is not necessary to obtain prior permission from the Patent Office to file patent application abroad:
(a) Applicant is not Indian resident and invention is originated abroad about.
(b) If the applicant is Indian resident and filed patent application has been in India before filing the application outside India and six weeks period is over from that date.
(c) The invention does not belong to Atomic Energy or defence purpose.
-
Under what circumstances, it is necessary to obtain a prior permission from the Patent Office?
- Residents of India require prior permission to apply for patents outside India under section 39 of the Patents Act, 1970 under following circumstances.
(a) The applicant or inventor is Indian resident,
(b) Applicant does not wish to file patent application in India prior to filing outside India.
(c) If the applicant is Indian resident, a patent application has been filed in India and six weeks period is not yet over from that date
(d) The invention relates to atomic energy or defence purpose.
However if the invention is relevant for Defence or Atomic Energy purpose, no permission shall be granted without the consent of Central Government.
-
Is there any additional requirement for filing of patent applications in respect of microbiological inventions?
- In addition to the various forms required to be filed at the time of filing the patent application, the applicant is also required to deposit the new strain of a microorganism if used in the invention disclosed in the patent specification, in a recognized depository which assigns a registration number to the deposited microorganism, before filing for the patent application. This number needs to be quoted in the patent application.
-
Are there any specific instructions to inventors in respect of filing for patent applications where their invention lies in biological material?
- The Patents Act, 1970 as well as the Biological Diversity Act, 2002 stipulates that the source and geographical origin of the biological material should be clearly disclosed in the patent specification. Further, according to the provision of Section 6 of the Biological Diversity Act, if the biological material used in the invention is from India, permission from the National Biological Authority has to be obtained by the applicant, and the same should be submitted to the Patent Office before the grant of patent.
-
Is it essential to deposit biological material in the international depository authority?
- If the invention uses a biological material which is new, it is essential to deposit the same in the International Depository Authority (IDA) prior to the filing of the application in India in order to supplement the description. The description in the specification should contain the name and address of the International Depository Authority and, date and number of deposition of Biological material. If such biological material is already known, in such case it is not essential to deposit the same. For more details log on to www.ipindia.nic.in
-
Is there any International Depository Authority in India?
- Yes, there is an International Depository Authority in India located at Chandigarh which is known as Institute of Microbial Technology (IMTECH). The more details regarding the said depository authority can be had on its website http://imtech.res.in/
-
Are there any restrictions with respect to the hearing adjournments?
- The Amended rules, 2016 provides for restriction on the number of hearing adjournments to two and each adjournment shall not be more than thirty days each. These adjournments have to be requested at least three days before the date of hearing.
-
What are the rights of a patentee once the patent is granted?
- A patentee enjoys the exclusive right to make and use the patented invention. The patentee also has the right to assign the patent, grant licences, or otherwise deal with the patent, for any consideration. These rights, created by statute, are circumscribed by various conditions and limitations as prescribed under the Patents Act.1970.
-
Is it necessary to show working of a patent after grant?
- Under the provisions of section 146, every patentee or a licensee, is required to furnish the information relating to working of patent, statement as to the extent to which the patented invention has been worked. This must be submitted on Form 27 by 31 March each year for the previous year ending 31 December.
-
What is the Budapest Treaty?
- This is an international treaty governing the deposition of microorganisms, cell lines etc in international approved authority approved by WIPO for the purpose of patent applications in any country that is a party to it. Because of the difficulties and, on occasion, of virtual impossibility of reproducing a microorganism from a description of it in a patent specification, it is essential to deposit a strain in a culture collection centre for testing and examination by others. There are many international depositories in many countries, which are recognised under the Budapest Treaty. IMTECH, Chandigarh is a recognised depository in India.
-
What are the modes of filing a patent application in foreign countries?
- Since there is no worldwide patent, the applicant has to file his patent application in respective countries separately to obtain protection on his invention. The following are the routes available to the applicant to file his International application in foreign country.
Paris Convention: The Paris Convention for the Protection of Industrial Property, established in 1883, provides for 12 months time to file the patent application in the member countries from the date of filing of the earliest application.
Patent Cooperation Treaty System: PCT is a system which allows an applicant to file in PCT contracting states within 30-31 months from priority date instead of 12 months. Not only does the PCT enable extended time period, it also simplifies filing procedure through a single application. The PCT system also provides for publication of application, International Search and International Preliminary Examination before entering the national phase .
-
What is the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT)?
- The PCT is an international treaty with more than 150 Contracting States which are bound with certain formal requirements set out in the Treaty and Regulations. The PCT makes it possible to seek patent protection for an invention simultaneously in a large number of countries by filing a single ―international‖ patent application instead of filing several separate national or regional patent applications however, granting of patents remains under the
control of the national or regional patent offices after the corresponding ―national phase‖ application has been filed and the national phase application is assessed as per patent law of that jurisdiction.
As per Indian Patent Act 1970 as amended and the Patents Rules 2003 as amended by (amendment) rules 2016, any PCT international application may be filed designating India and it shall deemed to be an application if the corresponding national phase application has also been filed.
-
What is the procedure of PCT?
- The PCT procedure includes:
A) Filing: File an international application with a RO/IN national patent Office or directly with International Bureau (IB) of WIPO, complying with the PCT formality requirements and fees. In India PCT application are filed at appropriate patent offices decided on the basis of territorial limits (Rule 4, Indian Patent Act 1970 as amended and patent Rules 2003 as amended).
B) International Search: An ―International Searching Authority‖ (ISA) identifies the published patent documents and technical literature (―prior art‖) which may have an influence on whether your invention is patentable, and establishes a written opinion on your invention‘s potential patentability. Indian Patent office, Delhi Branch performs the function of ISA on receipt of prescribed fee specified in Fifth Schedule of patent act 1970 as amended and patent rules 2003 as amended.
C) International Publication: After expiration of 18 months from the earliest filing date (Priority Date), the content of your international application is disclosed to the world.
D) International Preliminary Examination (optional): one of the ISAs on request carries out an additional patentability analysis, usually on an amended version of your application. Indian Patent office, Delhi Branch performs the function of International Preliminary Examination (IPEA) on receipt of prescribed fee specified in Fifth Schedule of patent act 1970 as amended and patent rules 2003 as amended.
E) National Phase: After the end of the international PCT procedure, usually at 30 months from the earliest filing date of your initial application, from which you claim priority, you start to pursue the grant of your patents directly before the national (or regional) patent Offices of the countries in which you want to obtain them.
F) TIme Limit: In India, 31 months is maximum time limit to enter national phase. To enter national phase an application corresponding to an international application is made in Form 1.
-
Who has the right to file an international patent application under the PCT?
- PCT international patent application may be filed by a national or resident of a PCT Contracting State. If there are several applicants named in the international application, only one of them needs to comply with this requirement.
-
Can I file PCT applications electronically?
- PCT applications can be filed electronically with RO/IN or RO/IB which accepts such filings (Indian Patent office does not accept full e- filling of PCT international application). WIPO web service (ePCT-filing) helps to prepare applications by automatically validating the
entered data and drawing your attention to incorrectly or inconsistently completed parts. Applicants are also entitled to certain PCT fee reductions when filing electronically (https://pct.wipo.int/). WIPO‘s PCT-SAFE software offers PCT user to prepare international application in electronic form (http://www.wipo.int/pct-safe/en/).
-
In which language can a PCT application be filed?
- PCT international application in India shall be filed with the appropriate office in triplicate either in English or Hindi. However, the request can be filed only in English.
-
What are the costs associated with the filing and processing of an international application under the PCT? What are the costs for entering the national phase?
- PCT applicants generally pay three types of fees when they file their international
applications:
(a) An international filing fee
(b) A search fee which can vary from ISA chosen, and
(c) A small transmittal fee which varies depending on the receiving Office.
Refer, Fifth Schedule of patent act 1970 as amended and patent rules 2003 as amended for fee structure for an international application designating India.
-
Are there any fee reductions available under the PCT?
- PCT fee reductions are available to applicants who file electronically, based on the type of filing and the format of the application submitted.
In addition, to encourage the use of the PCT System by applicants from developing countries fee reductions of 90% for certain fees, including the international filing fee, are available to natural persons. Some ISAs also provide for a reduction of the international search fee if the applicant or applicants are nationals or residents from certain countries (see Annex D of the PCT Applicant’s GuideWIPO).
-
How long does the PCT process take?
- 1) In most cases, up to an additional 18 months from the time you file your international patent application (or usually 30 months from the filing date of the initial patent application of which you claim priority) before starting of national phase procedures with individual patent Offices and to fulfill the national requirements.
2) This additional time can be useful for evaluating the chances of obtaining patents and exploiting invention commercially in the countries in which you plan to pursue patent protection, and for assessing both the technical value of your invention and the continued need for protection in those countries.
3) It is important to note, however, that you do not have to wait for the expiration of 30 months from the earliest filing date of your patent application (or priority date) before you enter the national phase – you can always request an early entry into the
national phase.
4) Since, in the national phase, each patent Office is responsible for examining your application in accordance with national or regional patent laws, regulations and practices, the time required for the examination and grant of a patent varies across patent Offices.
-
Will an international search be carried out for all international applications?
- i) As a rule, an international search is carried out for all international applications. There are instances, however, where the ISA will not be able to carry out a search.
For example, where the international application relates to subject matter which the ISA is not required to search or if the description, claims or drawings are not sufficiently clear for it to carry out a meaningful search. In such cases, the ISA will issue a declaration that no international search report will be issued.
ii) There are also circumstances where the ISA will issue a partial search report. This can occur when, in the view of the ISA, the international application contains multiple inventions but the applicant has not paid additional search fees to cover the work required to search those additional invention(s).
-
What are the advantages of the Patent Cooperation Treaty?
- The PCT System has many advantages for an applicant, for the patent Offices and for the general public:
(a) You have up to 18 months more than if you had not used the PCT to reflect on the desirability of seeking protection in foreign countries, to appoint local patent agents in each foreign country, to prepare the necessary translations and to pay the national fees;
(b) If your international application is in the form prescribed by the PCT, it cannot be rejected on formal grounds by any PCT Contracting State patent Office during the national phase of the processing of the application;
(c) The international search report and written opinion contain important information about the potential patentability of your invention, providing a strong basis for you to make business decisions about how to proceed;
(d) You have the possibility during the optional international preliminary examination to amend the international application, enter into dialogue with the examiner to fully argue your case and put the application in order before processing by the various national patent Offices;
(e) The search and examination work of patent Offices in the national phase can be considerably reduced due to the international search report, the written opinion and,
where applicable, the international preliminary report on patentability that accompany the international application;
(f) You may be able to fast-track examination procedures in the national phase in Contracting States that have PCT-Patent Prosecution Highway (PCT-PPH) agreements or similar arrangements;
g) Since each international application is published together with an international search report, third parties are in a better position to evaluate the potential patentability of the claimed invention;
(h) For an applicant, international publication online puts the world on notice of your invention. You may also highlight your interest in concluding licensing agreements on PATENT SCOPE, which can be an effective means of advertising and looking for potential licensees;
(i) You also achieve other savings in document preparation, communication and translations because the work done during the international processing is generally not repeated before each Office (for example, you submit only one copy of the priority document instead of having to submit several copies); and
(j) if your invention appears to be not patentable at the end of the international phase, you may abandon the PCT application and save the costs you would otherwise have incurred by directly seeking protection in foreign countries, appointing local patent agents in each foreign country, preparing the necessary translations and paying the national fees.
-
What is ePCT?
- ePCT is a WIPO online service that provides secure electronic access to the files of international applications filed under the PCT as maintained by the International Bureau. The applicants can file international applications using ePCT-Filing, with RO/IN as well as RO/IB.
-
What are the benefits of filing through ePCT?
- • Applicants can avail a fee reduction as fixed by PCT division of WIPO from time to time.
• Less cumbersome, for both RO as well as for the applicant.
• Fast processing
• Record copy transmitted to the IB on the same day